- JDK, JRE , JVM and architecture ( link)
- Classloader and its types (link)
- Java Args -X, -XX, -D link
- Java 8, 11, 17, 21 [LTS versions] best-link link link2
- Java memory [young, old, meta] This is genrational memory mgmt [link]
- Memory managment in Java and GC[link]
- Garbage collectors [ Types of GC:{Serial, parallel, CMS deprecated, G1GC[Default], ZGC, Shenandoah}] link
- G1GC(generational) vs ZGC(non generational memory mgmt, java 15) ?
- Thread Memory [thread memory]
- Local variable, instance variable, static variable difference?
- Why java is not pure object oriented language
- Object Oriented vs Object Based language
- Constructor (super, this) [link1]
- Characteristics of OOP (Encapsulation, Abstraction , inheritance, polymorphism) [link]
- Composition(has-a, loose couple) vs Inheritance(is-a, tight coupled)[link]
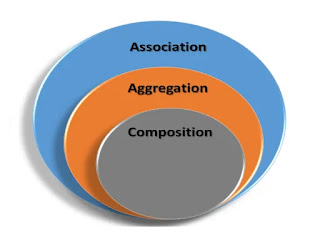
- Aggregation vs composition vs Association[link]
- Types of Polymorphism(static vs dynamic or overloading vs overrriding vs operator overloading) [link]
- Covariant Type and contravarient type [link]
- Interface vs Abstract
- Interface: default(java8) , private method(java9), static method(java9) [link]
- Exception Handling(checked and unchecked link[link2]
- String Constant pool link
- StringBuilder and StringBuffer
- Equals vs == [link]
- Equals and Hashcode [link]
- Reflection [link]
- Deep cloning vs shallow cloning
- Atomic Integer, Atomic long, Atomic boolean, Atomic ref
- Record, sealed, var sealed record var
- Inner Class and types [link]
- Serialisation and Deserialisation [Serial&Deserial]
- 1LserialversionUID link
- enum enum
- final, finally, finalize[final-java]
- transient,volatile[link]
- native[link] strictfp[redundant in java17]
- Java: passby value[passbyvalue]
- fail-fast, fail-safe [fail fast safe] [collection is fail fast]
- Process vs task link
- Thread [Introduction, wait notify ]
- Executor framework link
- ForkJoin vs ExecutorService link
- Runnable vs Callable (Thread)
- Future vs CompletableFuture(Thread result async)
- Functional Programming: Supplier, Consumer, Predicate, Function[functional program]
- Create singleton class while preventing reflection api link
- Comparable, comparator[link] link2
- Parallelstream vs stream link
- java8 flatmap [listoflist to list] link
- list to map in java 8+
- java8 stream().collect()::::: toMap,toSet link
- java8 Collectors [groupingby vs toMap] link
- Collectors partitionBy link
- Streams.sorted(), Collections.sort link
- Arrays.fill, Arrays.sort link
- Character to int conversion and vice versa link
- Collections, Collectors, Arrays,Math,Character
- ASCII value of a=97, A=65;
- Basic Into link
- HashTable [link] thread safe, method lock
- HashMap link1, link2 {uses linkedlist, then RB tree, not threadsafe hashtable}
- HashSet [link ]
- LinkedHashMap [link ] work as double linkedlist [array of doublinkedlist], maintain order
- LinkedHashSet [link]
- ConcurrentHashmap [link] is an extension of hashtable with better synchronised version than hashtable[segment lock instead of methd or block lock]
- TreeMap: internally uses RB Tree [link]
- TreeSet: The data structure for the TreeSet is TreeMap; it contains SortedSet & NavigableSet interface to keep the elements sorted in ascending order and navigated through the tree.
- Why hashmap with custom key object immutable?? For sorting hashmap has customer object as key should be immutable object because of this reason string is preferred as key
- Sort hashmap by values.link
- Hashtable{method level locl} vs synchronisedhashMap{block level lock also supported} vs concurrenthashmap{segment lock} vs linkedhashmap vs treemap link
- Heap data structure[min heap and max heap]
- PriorityQueue is important data structure[default is min heap, use arraylist internally] link
Thread and synchronization
- Basic Intro link with detail
- Concurrency vs Parallelism [link]
- Types of synchronisation: static sync, sync block, sync method
- Object: wait, notify, notifyAll. [Inter Thread communication link]
- Thread: yield, join link.
- Threadpool example link
- Two thread accessing synchronise method
- Cyclic Barrier vs CountDownLatch link
Aggregation: A weak relationship where one object contains another but the contained object can exist independently.
Composition: A strong relationship where one object contains another, and the contained object cannot exist without the container.
Inheritance: A class inherits properties and behavior from another class.
Spring Boot Framework
- Sync, Async, Reactive programming
- Spring IOC container(ApplicationContext interface) link
- Dependency Injection types: constructor, setter, field based DI
- Bean scopes link1 link2
- Bean lifecyle link
- Dispatcher servlet link
- @Controller, @RestController, @Service,@Repository link
- Lazy loading link
- Spring multiple datasource link link2 link3
- Load time invoking functionality link2 link1
- Spring webflux link link2
- How to create custom annotation in spring boot?
- how to implement rate limiter in spring boot
- How to implement security in spring boot?
- Spring JPA link link2 [used for JDBC]
- Spring R2dbc link link [prefered ]
- Spring Webclient link
- Spring transaction mgmt link
- Spring batch processing link link2
- Spring logging framework(logback is default) link
- Spring exception handling link
- Spring testing framework link
- @Springbootapplication annotation
@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan,@Configuration - Spring swagger [openapi documentation- latest] link
- Spring redis link1 lettuce link 2
- Spring kafka link
- Spring AOP link
- Spring boot security with JWT link
- Spring security intro basic weblfux oauth2 jwt
- Put vs post vs patch link
- Commandline runner vs Applicationrunner link
- Spring elastic searchlink
Authentication & Authorisation Framework
- Resource server, client server, Authorisation service
- OAuth2 is an Authorisation framework whereas,
OpenId is layer on top of oauth2 to provide authentication (Authentication + Authorisation ). - OAuth Grant types:
- Authorization Code (web app mostly)link
- PKCE(mobile or any app, it is an extension of authorisation code)link link2
- Client Credentials (service account or service to service]link
- Device Code (apps auth via authenticator or authentication in smart tv) link
- Implicit Flow(legacy and not recommended)
- Password Grant(legacy and recommended)
- JWT [Its format of token used, can be used in Authentication and authorization, auth code , accesstoken are sent as jwt token] link. Other token can be opaque token. JWT is self contained token
- Claims in JWT(registered, public, private)
- Client side best practice for cookie link [Since we are trying to protect our application as much as possible from hacking, we must store our refresh token exclusively in an HttpOnly Cookie.]
Note: - Auth and types link
- Http headers
- X509 certificate
- OAuth Detail description and usage
- Which OAuth should I use link
- OAuth Examples with diagram good example
- SAML vs OAuth vs JWT vs OpenId link
- OAuth vs JWT link
- SAML (enables SSO, multiple app with one auth)
Authentication Framework
Authentication vs Authorisation
Application in Microservice :
******************************************************************************
React and Redux
- Hello world Concept example webpack example
- React VirtualDom link
- Virtual DOM vs Shadow DOM link
- Reconciliation: diffy algo in fibre node
- Higher order components link
- hoisting link
- let vs var link [hoisting happens in var]
- API call (axios) link
- Webpack link link2
- Babel link
- useMemo, useCallback, useContext link
- Redux::: action , store, dispatcher, reducer [useReducer] Explaination
- CORs for protection
- Testing framework for FE testinglib link enzyme
- React vs Angular vs vue link
- Typescript link
- Microfrontend design link Eg:Module federation, single-spa
- Def between useRef and useState link [useref doesnt cause re rerendering of page]
- useMemo vs useCallback [useCallback hook memoizes function itself, not its return value like use memo]
- type vs interface in typescript
- interface vs class
- Jest: Best for unit testing and snapshot testing with easy configuration
- Mocha: Best for flexible, customizable test setups with asynchronous support
- Enzyme: Best for testing React component internals with shallow and full rendering
- TestCafe: Best for cross-browser testing and end-to-end testing with simple setup
- Jasmine: Best for behavior-driven development (BDD), focusing on simplicity
- Chai: Best for expressive assertions in tests using BDD/TDD style
- Cypress: Best for fast, reliable end-to-end testing with real-time browser interaction
- Puppeteer: Best for headless browser automation and UI testing
- React Testing Library: Best for testing React components through user interactions
- Sinon: Best for mocking, spying, and stubbing external dependencies in tests
- Nightwatch.js: Best for simple end-to-end testing with WebDriver integration
- QUnit: Best for straightforward unit testing, especially in legacy projects
- Storybook: Best for visually testing and documenting UI components in isolation
- Ava: Best for fast, concurrent testing with minimal configuration
- Detox: Best for end-to-end testing of mobile apps, particularly React Native, with fast test execution.
Note- The algorithm React uses to diff one tree with another to determine which parts need to be changed also k/a reconciliation. .JavaScript is a dynamically typed language. In a dynamically typed language, the type of a variable is checked during run-time in contrast to a statically typed language, where the type of a variable is checked during compile-time.In JavaScript, primitive data types are passed by value and non-primitive data types are passed by reference.Functions that operate on other functions, either by taking them as arguments or by returning them, are called higher-order functions.Memoization is a form of caching where the return value of a function is cached based on its parameters. If the parameter of that function is not changed, the cached version of the function is returned.
SQL
- Groupby and having link
- Explain the differences between SQL and NoSQL databases.
- Types of join link
- SQL vs PSQL vs TSQL link
- Unique key vs Primary key
- Where vs Having in sql
- Delete, truncate, drop [Drop removes table structure as well, truncate for all data]
- SQL INTO
- Nth highest salarylink
- On delete cascade
- How do you optimize SQL queries? link1 link2
- How do u handle transaction in distributed system [SAGA, 2PC]
- How do you prevent SQL injection link
- Concept of sharding link
- Concept of partitioning link
- SQL concept quesn link
- SQL query query interview
- SQL query to find last 3 month data
JOINis a shorthand forINNER JOINin PostgreSQL- How to choose right DB ? link
SELECTFROMWHEREGROUP BYHAVINGORDER BY
Question:
You are given 2 database table. First table named as 'goals' with fields as goal_id, player_id, team_id, goal_time.
Second table names as 'teams' with field name as team_id, team_name.
Write a sql query to fetch the name of all teams that scored atleast one goal within 30sec of time and also corresponding count count of goals with respect to teamYou are given 2 database table. First table named as 'goals' with fields as goal_id, player_id, team_id, goal_time.
Second table names as 'teams' with field name as team_id, team_name.
Write a sql query to fetch the name of all teams that scored atleast one goal within 30sec of time and also corresponding count count of goals with respect to team . Also show result in order of highest goal to lowest in descending order
Ans:
SELECT column1, column2, ... INTO new_table_name FROM existing_table WHERE condition;
SELECT employees.emp_name, departments.dept_name FROM employees JOIN departments ON employees.dept_id = departments.dept_id;
Note:
Managing large-scale databases for performance involves various strategies, including proper indexing, partitioning, query optimization, hardware optimization, and caching. Monitoring and fine-tuning the database is crucial to ensure optimal performance as data volumes grow.
Ensuring data availability and disaster recovery relies on the implementation of vital backup and recovery strategies. These strategies encompass various methods, such as full backups, differential backups, transaction log backups, and regular testing of restoration procedures.
NoSQL databases are non-relational databases designed for handling large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. They interact with SQL databases through various integration methods, such as data pipelines, ETL processes, and API-based data transfers
Advanced optimization techniques for SQL queries include using query hints, indexing strategies, query rewriting, and understanding the query execution plan. Profiling tools and performance monitoring are essential for identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks
The INTO clause creates a new table, not just inserts data into an existing one
SOLID principle
Single Responsibility Principle | Each class should be responsible for a single part or functionality of the system |
Open-Closed Principle | Software components should be open for extension, but not for modification. |
Liskov Substitution Principle | Objects of a superclass should be replaceable with objects of its subclasses without breaking the system. |
Interface Segregation Principle | No client should be forced to depend on methods that it does not use. |
Dependency Inversion Principle | High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules, both should depend on abstractions. |
*************************************************
Design Pattern in Java(GOF pattern)
Design patterns are typical solutions to commonly occurring problems in software design. They are like pre-made blueprints that you can customize to solve a recurring design problem in your code. Usage examples in java link- Creational Design pattern: are concerned with the way of creating objects.
Singleton, Builder, Factory pattern, Abstract Fcatory link link2 - Structural Design pattern : These patterns explain how to assemble objects and classes into larger structures while keeping these structures flexible and efficient.
Adopter, Decorator, Facade, Composite, Bridge, flyweight design pattern link - Behavioural Design pattern : are concerned with the interaction and responsibility of objects.
Observer, Iterator, ChainOfResponsibility, Strategy, Command linkExtra: link
Microservice Design Pattern
Microservices is an architectural style for building applications as a collection of independent services. Each service is built and deployed independently, and can be scaled independently
use chatgpt directly to study about all
*************************************************
System Design round
************************************************
Additional Topic Note:
- Architect Interview javafungus
- Data Engineering javafungus
- Databases javafungus
- Reverse proxy vs forward proxy
- Brownfield vs greenfield microservice app development
- KISS, DRY, SOLID, YAGNI link
- Code review link
- Component Cohesion & Coupling link
Implement OAuth 2.0 authentication for a Spring Boot REST API using JWT tokens
Name any recent cyberattack you heard of